Computer Architecture
A computer consists of the following components:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- DMA Controller (Direct Memory Access)
- Memory (Normally RAM, Random Access Memory)
- Timer
- Device Controller

CPU
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is a computer component structured as follows:
It is a worker that simply interprets and executes instructions stored in memory, triggered by *interrupts.
When the kernel of the operating system (the manager) loads a program into memory and turns it into a process, the CPU (the worker) processes it.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)_산술논리연산장치 - The ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) is a digital circuit that performs arithmetic operations (like addition and subtraction) and logical operations (like XOR and AND) between two numbers.
- Control Unit (CU)_제어장치 - The Control Unit (CU) is a part of the CPU that directs the operations of the processor. It controls communication between input/output devices, reads and interprets instructions, and determines the sequence of data processing.
- Registers - Registers are very fast, temporary storage units inside the CPU. Since they are directly connected to the CPU, their operation speed is tens to hundreds of times faster than main memory. Because the CPU has no inherent way to store data, it uses registers to transfer and hold data temporarily.
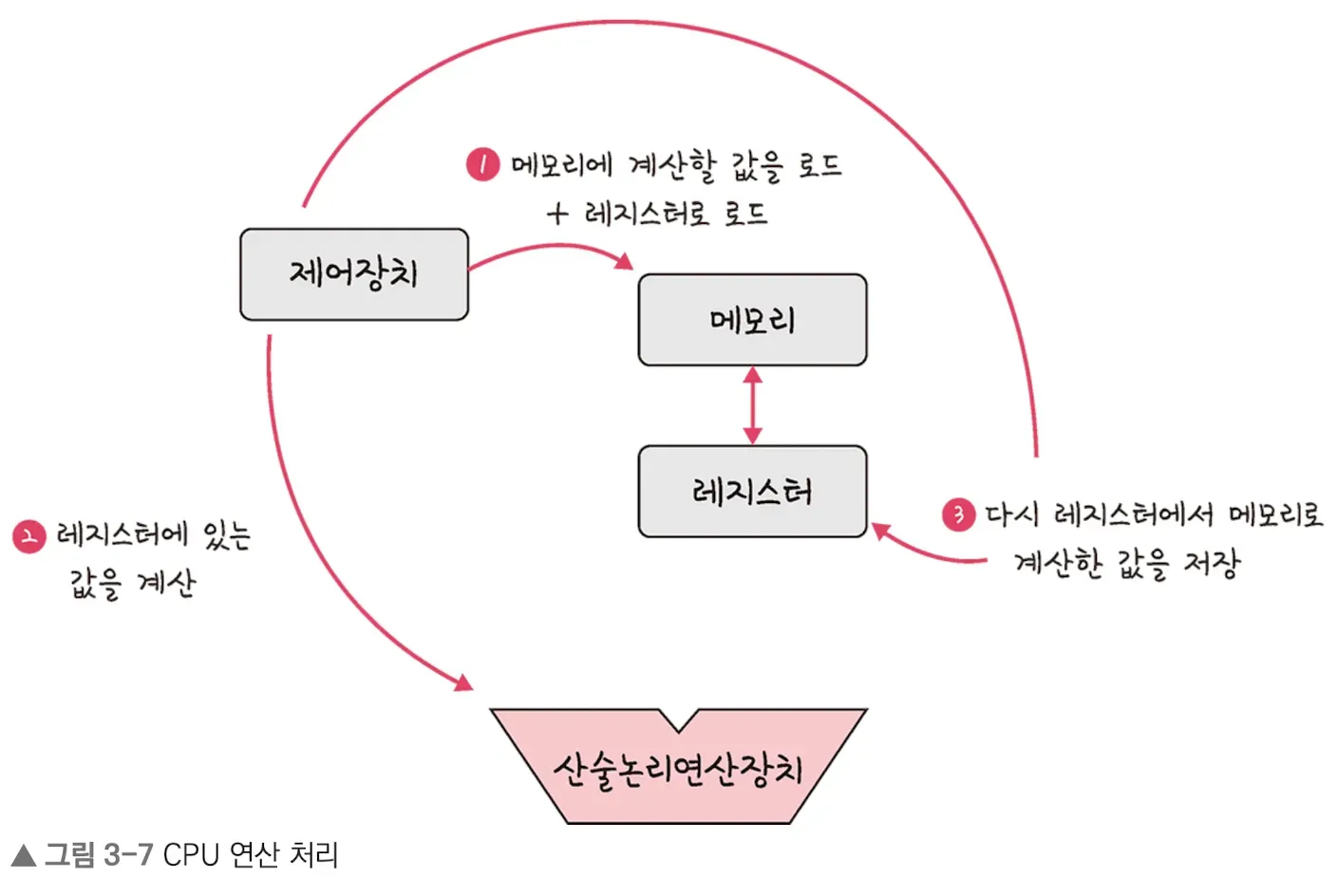
- The Control Unit (CU) loads the value to be computed from memory and also loads it into the registers.
- The Control Unit instructs the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) to perform calculations on the values stored in the registers.
- The Control Unit stores the computed result back from the register into memory.
*Interrupt
An interrupt refers to temporarily pausing the CPU when a specific signal is received.
Interrupts have priorities and are executed based on their priority.
There are two main types of interrupts: hardware interrupt and software interrupt.
- Hardware Interrupt
- Triggered by I/O devices such as when connecting a keyboard or mouse.
- These interrupts are generated by hardware signals from external devices.
- Software Interrupt
- Also called a trap.
- Triggered when a process calls the system, often due to a process error or a specific system call.
DMA (Direct Memory Access) Controller
- Manages data transfer between memory and I/O devices without involving the CPU, thereby improving system performance.
- It is a hardware device that allows I/O devices to access memory directly.
- Acts as an assistant to the CPU by offloading the heavy load of frequent interrupt requests.
- Prevents the CPU and the DMA controller from working on the same task simultaneously.
Memory
- Memory refers to a device in electronic circuits that stores data, state, or instructions.
- Commonly refers to RAM (Random Access Memory).
- The CPU handles computation, while memory handles storage.
Timer
- The timer sets a time limit on certain programs, ensuring that tasks complete within a specified time frame.
- Used to prevent long-running programs from monopolizing resources.
Device Controller
- The device controller is essentially a small CPU dedicated to managing I/O devices connected to the computer.
'Computer Science > Operating System' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Process (0) | 2025.07.30 |
|---|---|
| How memory manages data (0) | 2025.07.27 |
| Memory (0) | 2025.07.25 |
| Structure of the Operating System (0) | 2025.07.19 |
| What is an operating system? (0) | 2025.07.16 |