One of the key roles of an operating system is memory management.
It must maximize the use of limited memory resources inside the computer.
Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is a memory management technique that
abstracts the actual physical memory resources available on a computer
and makes it appear as a very large memory to the users.
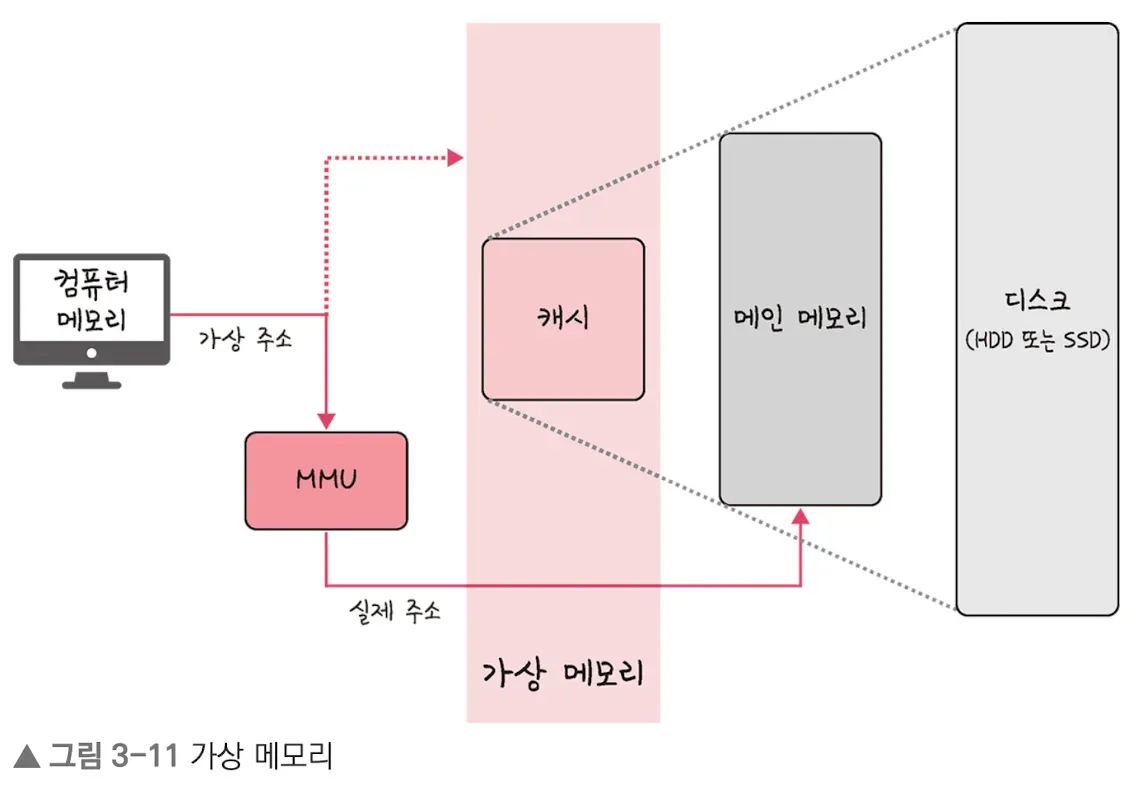
- The virtual addresses given are called virtual addresses (logical addresses),
- while the addresses physically present in memory are called physical addresses.
- Virtual addresses are translated to physical addresses by the Memory Management Unit (MMU),
- which allows users to develop programs without needing to be aware of the physical addresses.
- Virtual memory is managed through a page table that maps virtual addresses to physical addresses and contains the address information of processes.
More about Virtual Memory – Reasons for Use, Pros and Cons
Virtual memory is a technology in computer systems that expands the capacity of the actual physical memory (RAM). This allows the computer to keep and process data larger than the physical memory. Virtual memory works by using a portion of the disk space as if it were additional memory.
Why Use Virtual Memory?
- Efficient Memory Usage - Although the actual physical memory (RAM) size is limited, virtual memory provides a larger memory space by using disk space, allowing programs to operate as if they have more memory.
- Process Isolation - Each process uses its own virtual memory space, preventing one process from accessing or corrupting another process’s memory.
- Support for Multitasking - When multiple programs run simultaneously, virtual memory allows each program to behave as if it has sufficient memory, effectively supporting multitasking.
- Running Large Programs - Even when physical memory is insufficient, virtual memory enables running larger programs or handling large-scale data tasks.
Advantages
- Solves Memory Shortage - Programs can continue to run without interruption by using part of the disk as memory when physical memory is low.
- Improves Multitasking - Prevents memory conflicts among programs running simultaneously and allocates resources efficiently.
- Enhances Safety and Security - Since each process has its own virtual memory space, interference between processes is prevented, increasing system stability.
- Improves System Performance - Less frequently used memory areas can be paged out to disk, freeing up more memory for active data.
Disadvantages
- Speed Degradation - Because virtual memory uses the disk, it is slower than RAM. Frequent disk access can cause performance drops (swapping).
- Disk Space Usage - Using disk as memory consumes significant disk space.
- Increased Complexity - Managing virtual memory requires additional system resources such as page replacement algorithms and page tables, making system management more complex.
Summary
Virtual memory is a technique that extends physical memory, enhancing system efficiency and enabling large program execution. However, it has downsides like speed degradation and excessive disk space usage.
Swapping
When accessing data or code that exists in virtual memory but is not currently in physical memory (RAM), a *page fault occurs.
At this point, the OS moves unused areas of memory to the hard disk and loads the required part of the disk into memory as if it were RAM — this process is called swapping.
*Page Fault
A page fault occurs when a process tries to access data that exists in its virtual address space but is not currently loaded in the computer’s RAM.
Page Fault and the Resulting Swapping
- The CPU checks physical memory and, if the page is missing, triggers a trap (software interrupt) to notify the OS.
- The OS pauses the CPU.
- The OS checks the page table to see if the page exists in virtual memory.
- If it does not exist, the process is terminated.
- If it exists but no free frame is available in physical memory, swapping is triggered.
- The page is loaded into a free frame in physical memory, and the page table is updated.
- The CPU resumes its operation.
Page: The smallest unit of virtual memory.
Frame: The smallest unit of physical memory.
Thrashing
Thrashing refers to a state where the page fault rate is very high, severely degrading the system’s performance.
Memory Allocation
When allocating memory to a program, the OS determines the starting memory location and allocation size.
This can be done using two methods: contiguous allocation and non-contiguous allocation.
- Contiguous Allocation - Allocates memory in one continuous block.
- Non-contiguous Allocation - This is the method used by modern operating systems, with various techniques for efficient non-contiguous allocation. Allocates memory in scattered blocks rather than continuously.
'Computer Science > Operating System' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PCB & Context Switching (0) | 2025.08.03 |
|---|---|
| Process (0) | 2025.07.30 |
| Memory (0) | 2025.07.25 |
| Components of a computer (0) | 2025.07.22 |
| Structure of the Operating System (0) | 2025.07.19 |